Diabetic Retinopathy
If you have Diabetes, you need to pay special attention to your EYES before it is too late. Failing vision could be the first sign of damage being caused to your vital organs due to diabetes. Dadar eye clinic with its latest and finest treatment is the preferred place for you to address your Diabetic Retinopathy (damage caused to retina)
Resources On Diabetic Retinopathy:
- What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
- What are the symptoms of diabetic Retinopathy?
- Key points to Remember
- How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
- Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
- What are the current treatment options for a person with diabetic retinopathy?
- Why prefer dadar Eye For Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment?
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Patients with diabetes are more likely to develop eye problems such as cataracts and glaucoma, but the disease’s affect on the retina is the main threat to vision. Most patients develop diabetic changes in the retina after approximately 5-20 years. The effect of diabetes on the eye is called diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in young and middle-aged adults today. The longer a person has diabetes, the greater their chance of developing diabetic retinopathy. There are two types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
NPDR, also known as background retinopathy, is an early stage of diabetic retinopathy and occurs when the tiny blood vessels of the retina are damaged and begin to bleed or leak fluid into the retina resulting in swelling (diabetic macular edema) and the formation of deposits known as exudates. Many people with diabetes develop mild NPDR often without any visual symptoms.
PDR carries the greatest risk of loss of vision and typically develops in eyes with advanced NPDR. PDR occurs when blood vessels on the retina or optic nerve become blocked consequently starving the retina of necessary nutrients. . New, fragile, vessels develop as the circulatory system attempts to maintain adequate oxygen levels within the retina. This is called neovascularization. Unfortunately, these delicate vessels hemorrhage easily. Blood may leak into the retina and vitreous, causing spots or floaters, along with decreased vision.

PDR may lead to any one of the following:
- Vitreous hemorrhage – proliferating retinal blood vessels grow into the vitreous cavity and break down. Both the hemorrhaging and resultant scar tissue may interfere with vision.
- Traditional retinal detachment – scar tissue in the vitreous and on the retina cause the retina to detach.
- Tractional and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment – scar tissue creates a hole or tear in the retina causing it to detach.
- Neovascular glaucoma – abnormal blood vessel growth on the iris blocks the flow of fluid out of the eye causing the pressure to increase and damaging the optic nerve.

What are the symptoms of diabetic Retinopathy?
Generally, people with mild NPDR do not have any visual loss. A dilated eye exam is the only way to detect changes inside the eye before loss of vision begins. People with diabetes should have an eye examination at least once a year. More frequent exams may be necessary after diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed.
People with PDR experience a broader range of symptoms. They may:
- See dark floaters
- Experience loss of central or peripheral vision
- Experience visual distortions or blurriness
- Experience temporary or permanent vision loss
Key points to Remember
- If you have diabetes, or a family history of diabetes, you need to pay special attention to your EYES before it is too late.
- Failing vision could be the first sign of damage being caused to your vital organs due to high sugar levels.
- There are no signs or symptoms in early stages
- It starts with bkurred vision causing problems while reading or driving.
- Gradually as the blood vessels leak , it feels like black spekcs or patch floating in the eye which may or may not go away.
How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
Diabetic Retinopathy is diagnosed by :
- Indirect OPhthalmology: Dilated retinal examination : dilating the pupil and looking inside the eye with an ophthalmoscope. If an ophthalmologist discovers diabetic retinopathy, he or she may wish to order color photographs of the retina through a test called fluorescein angiography.
- FUNDUS FLUORESCEIN ANGIOGRAPHY (FFA): During this test, a dye is injected into the arm and quickly travels throughout the blood system. Once the dye reaches the blood vessels of the retina, a photograph is taken of the eye. The dye allows the ophthalmologist to detect damaged blood vessels that are leaking dye.
- Retinal Colour photography (with Imagenet)
- Optical coherence tomographyC.T Macula → For High resolution cross sectional images of eye/retina
- B Scan→ To Detect Retinal Detachment and Vitreous hemorrhage


Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
The most effective overall strategy for diabetic retinopathy is to prevent it as much as possible. Researchers have found that diabetic patients who are able to maintain appropriate blood sugar levels have fewer eye problems than those with poor control. Diet and exercise play important roles in the overall health of those with diabetes.
Diabetics can also greatly reduce the possibilities of eye complications by scheduling routine examinations with an Ophthalmologist. Many problems can be treated with much greater success when caught early.


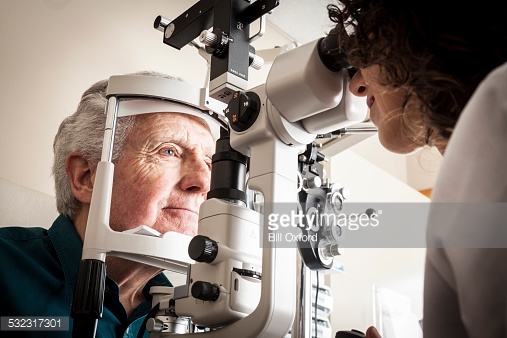
If you have Diabetes make sure that you get a Dilated Retinal Examination at least once a year to prevent Vision Loss.
Early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy is the best protection against Loss of VisionBetter control of blood sugar levels slows the progressive of the disease and lowers the risk of vision loss.
What are the current treatment options for a person with diabetic retinopathy?
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is treated in many ways depending on the stage of the disease and the specific problem that requires attention. The retinal surgeon relies on several tests to monitor the progression of the disease and to make decisions for the appropriate treatment. These include: fluorescein angiography, retinal photography, and ultrasound imaging of the eye.
1 Green Laser For PRP / Macualr Grid / Barrage etc

Patients with diabetes are at greater risk of developing retinal tears and detachment. Tears are often sealed with laser surgery. Retinal detachment requires surgical treatment to reattach the retina to the back of the eye. The prognosis for visual recovery is dependent on the severity of the detachment.
2. Vitrectomy For Posterior Capsule
Vitrectomy is commonly needed for diabetic patients who suffer a vitreous hemorrhage (bleeding in the gel-like substance that fills the center of the eye). During a vitrectomy, the retina surgeon carefully removes blood and vitreous from the eye, and replaces it with clear salt solution (saline). At the same time, the surgeon may also gently cut strands of vitreous attached to the retina that create traction and could lead to retinal detachment or tears.
Advised to patients for conditions like Rent, / Vitreous Hemorrhage / Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy / Retinal Detachment etc.
FACILITIES AVAILABLE AT dadar eye clinic
- Slit lamp Delivery system
- Indirect OPhthalmology → To evaluate Retina
- F.F.A → For Angiography of Retina
- Retinal Colour Photography → with Imagenet
- O.C.T Macula → For High resolution cross sectional images of eye/retina
- B Scan → To Detect Retinal Detachment and Vitreous hemorrhage
Treatment:
- Laser Treatment → Green Laser * Retinal Laser for PRP
- Intravitreal Injections
- Vitrectomy → for different kinds of Retina Surgeries
fully equipped with the latest technology and highly qualified experienced Vitreo Retinal Specilaists for the diagnosis and treatment of all retinal ailments.
Topcon Imagenet Retinal Imaging System for coloured photography of Retina
Digital Fundus Camera for Fundus Fluoroscien Angiography (FFA) and Fundus Photography – This is connected to image net software for easy Archiving and retrieval of Photographs and instant reporting.
Frequency doubled ND -YAG Laser (Green Laser) – It is used for treatment of disease like Diabetics Retinopathy, Vascular Occlusions and peripheral retinal degenerations. It fully equipped with three delivery systems

